About BIOMONDO
On this page:
Biodiversity+ Precursors
The European Space Agency (ESA) activity called Biodiversity+ Precursors is a contribution to the joint EC-ESA Earth System Science Initiative launched in February 2020 to jointly advance Earth System Science and its response to the global challenges that society is facing in the onset of this century. The ESA Biodiversity+ Precursors include three projects on different themes; land (EO4Diversity), coast (BiCOME) and freshwaters (BIOMONDO). BIOMONDO is the freshwater project, and has a focus on biodiversity in lakes, wetlands, river and streams.
EO4Society is a programmatic element of the ESA FutureEO-1 programme, which aims at boosting Europe’s excellence in Earth Observations systems, application and science, with other scientific disciplines and latest advances in ICT technologies, to maximise impact and benefits for society. It supports the development of innovative EO solutions that transform satellite measurements into information products for improved scientific knowledge and evidence-based decisions. This is pursued by advancing the use of satellite observations in Earth System Science and by pioneering novel EO applications, including algorithm development and pre-commercial services, ready to be deployed into the digital platform economy.
To put words into practice, four joint EC-ESA Flagship Actions have been selected for kick-off in 2020-2021 (i.e., Polar changes and global impacts, Biodiversity and vulnerable ecosystems, Ocean health, Climate adaptation to extremes and natural disasters). Implementation of these flagship actions is based on a co-programmed approach ensuring the coordination of relevant scientific activities, calls, and work plans initiated under EC’s Horizon Europe and ESA’s FutureEO programmes, respectively. The Biodiversity+ Precursors activity represents the first contribution from the European Space Agency to the EC-ESA Flagship Action on Biodiversity and Vulnerable Ecosystems.
BIOMONDO Objectives
- Identify the main science challenges (including observation gaps) in Earth Observation for biodiversity in freshwaters
- Develop and validate a set of innovative EO-based methods and a portfolio of novel EO products to address these gaps and challenges
- Combine the portfolio of novel EO products with ecological field data, advanced biodiversity modelling and modern data analytics techniques into innovative integrated scientific solutions
- Showcase, in close collaboration with a number of early adopters, the next generation of decision support systems
- Develop a Science Agenda and a Scientific Roadmap for EO supported biodiversity assessments in freshwaters
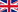
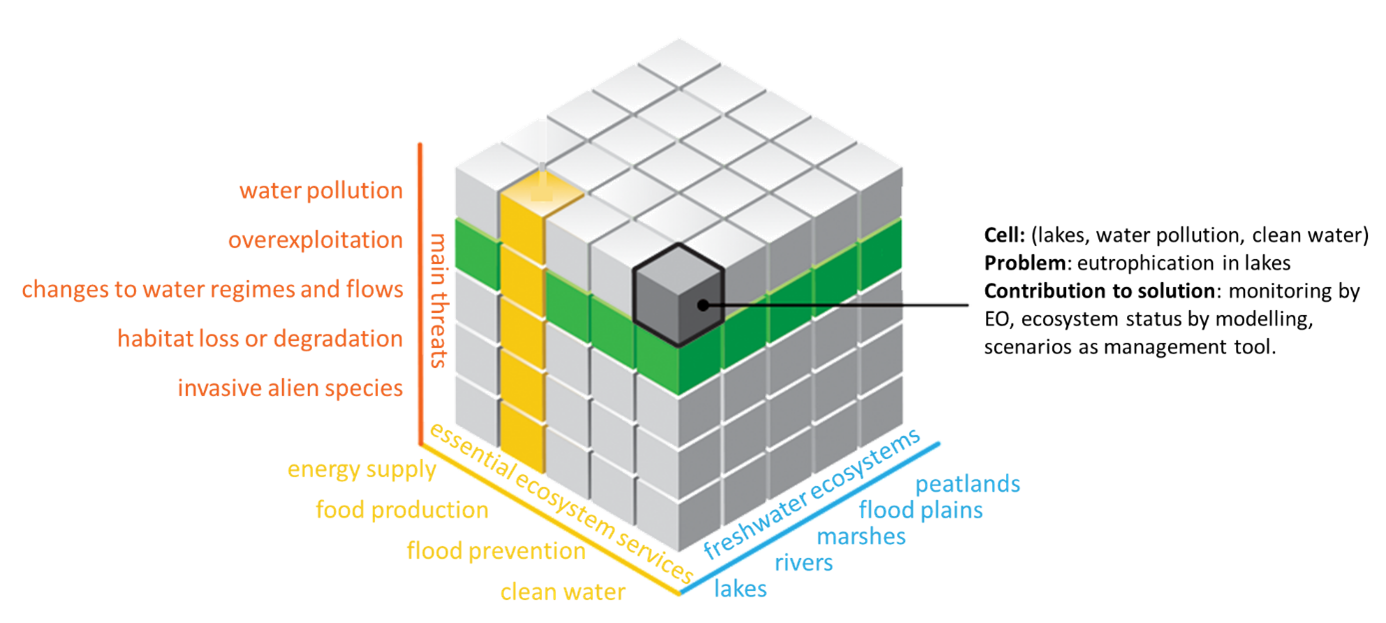 Figure. Multi-dimensionality of the challenge to understand, assess and predict freshwater ecosystems status and evolution.
Figure. Multi-dimensionality of the challenge to understand, assess and predict freshwater ecosystems status and evolution.
Pilot studies
The purpose of the biodiversity pilot studies is to explore if Earth Observation (EO) products in combination with models and in situ data can support freshwater biodiversity monitoring and management.
Pilot studies will be implemented at selected sites for specific scientific objectives and demonstrated for relevant policies.
The pilot studies and sites have been selected where biodiversity expertise, ecological and ecosystem models, and historical in situ data are available to validate the scientific utility and impact of novel EO products. The potential for upscaling to a high, preferably global, geographic scale has also been considered. Special priority has been given to sites of particular importance for nature conservation and where environmental changes have occurred in the last decades.
Based on the scientific pilot results, showcases will be developed to demonstrate the policy utility and impact of the novel EO products. The potential for integration into decision support systems and enhanced biodiversity management will be assessed together with Early Adopters (stakeholders).
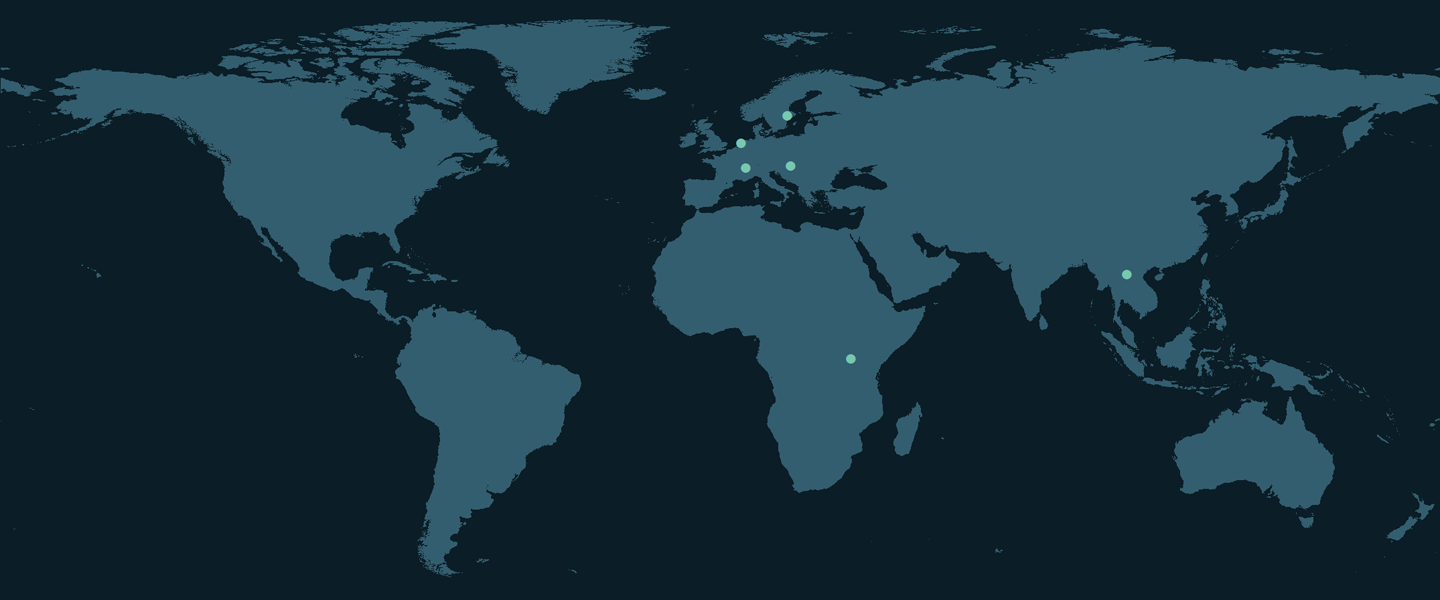 Figure. BIOMONDO pilot sites.
Figure. BIOMONDO pilot sites.
Pilot 1
The impact of eutrophication and habitat changes on the water quality of shallow lakes.
Detailed Pilot 1 information can be found here: BIOMONDO_Pilot1.pdf
Nutrient concentrations have increased substantially in lakes and rivers throughout the world. This has resulted in eutrophication, changes in water column trophic status, harmful algal blooms, loss of submerged macrophytes affecting sedimentation and turbidity, changes in seasonal dynamics (phenology) and subsequent biodiversity loss.
The pilot objective is to explore the possibilities with EO and integration of EO data into hydrodynamic and bio-geochemical models to monitor changes in water quality and impact on biodiversity of habitat improvement measures.
Summary of results: BIOMONDO_Science_Brief_Pilot1.pdf
Pilot 1 - site
The IJsselmeer area is the primary site for Pilot 1 as it is an important site to study (reverse) eutrophication and habitat changes on biodiversity.
Several measures have been implemented to provide sheltered habitats for the development of macrophytes, (spawning) fish, and other species at higher trophic levels. One of these measures is the creation of islands (Marker Wadden), that also aim to improve the water quality of Lake Markermeer for red listed and other aquatic herbivorous, fish-eating, and mussel-eating waterfowl. With EO we can detect these changes in habitat type to complement our analysis.
Pilot 1 - showcase
Policy Relevance:
- Water Framework Directive (WFD)
- Essential Biodiversity Variables (EBVs)
The implementation of the European WFD is based on biological quality factors and supporting physio-chemical properties. EO can provide reliable and quantitative measurements of e.g. chlorophyll a and Secchi Disc Depth, which are parameters related to these factors. The EBVs focus on status and trend of several biodiversity elements and should serve as the first level of abstraction between low-level primary observations and high-level indicators of biodiversity.
The outcome of the pilot will be used to demonstrate how the results can support WFD ecological status classification and actions, as well as the EBV elements productivity and phenology assessment. Algal blooms and cyanobacteria presence can be identified in EO data and is probably the only way to map coverage, length, frequency and amplitude of algal blooms in a good way.
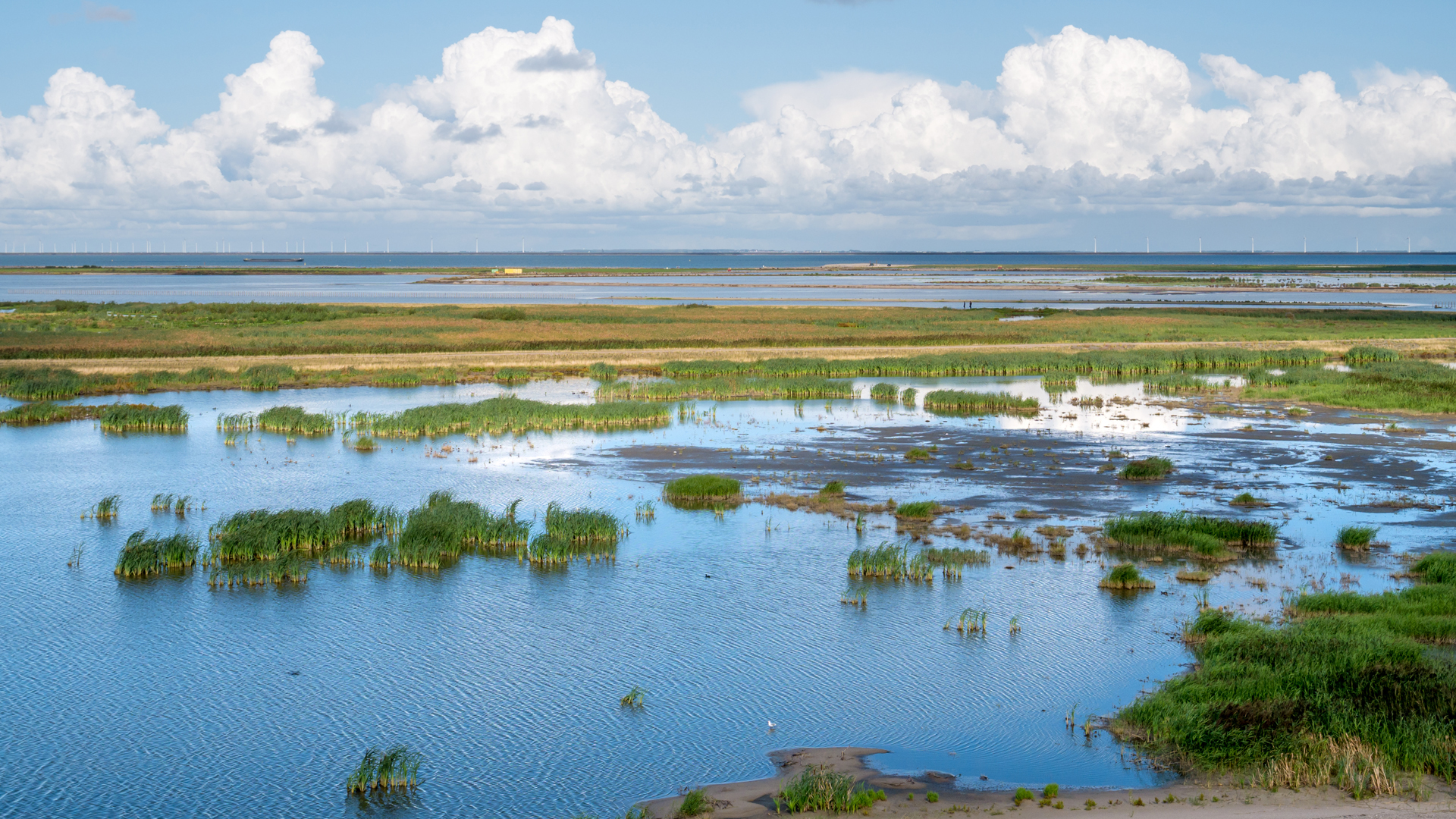 Figure. Marshes on the manmade artificial island of Marker Wadden, Markermeer, Netherlands.
Figure. Marshes on the manmade artificial island of Marker Wadden, Markermeer, Netherlands.
Pilot 2
Impact of changes in water temperature and heat waves on freshwater fish diversity.
Detailed Pilot 2 information can be found here: BIOMONDO_Pilot2.pdf
Global lake surface water temperatures have been rising in the last decades and the duration and intensity of lake heat waves are expected to increase with future climate change. Lake and river ecosystems are vulnerable to these temperature changes both directly, by pushing to or exceeding species and ecosystems limits of resilience, and indirectly, by decreasing the amount of oxygen in the water and altering stratification.
The pilot objective is to explore the possibilities of using a combination of EO based surface water temperature (SWT) and a thermal tolerance model of freshwater fish species to quantify the impacts of increases in long-term water temperature and frequency and intensity of heat waves on fish diversity.
Summary of results: BIOMONDO_Science_Brief_Pilot2.pdf
Pilot 2 - site
Lakes Balaton, Geneva, Markermeer, Mälaren and Victoria have been selected as test sites for this pilot. The selection was made based availability of in-situ temperature and fish data, such as species composition and abundance. In addition, heat wave related fish kills have been observed in Lake Mälaren and Victoria, during the last five years.
Pilot 2 - showcase
Policy Relevance:
- IPBES work programme (IPBES WP)
- Water Framework Directive (WFD)
The new IPBES work programme (2019-2030) includes a thematic assessment, which will examine interlinkages between biodiversity, water, food, energy and health in the context of climate change and human health. The implementation of the European WFD is based on biological quality factors, and climate-related threats and adaptation must be considered. 'Fish' is one of these WFD quality factors and information on abundance, species composition and age structure of all fish present in a water body are required.
The outcome of the pilot will be used to demonstrate how the results can support WFD assessments of impact on fish biodiversity and abundance from increasing water temperature and short-term heat waves related to climate change. It will also be explored if the results can support the analysis of interlinkages between climate change and food and water shortages, biodiversity loss and spread of disease according to the IPBES WP.
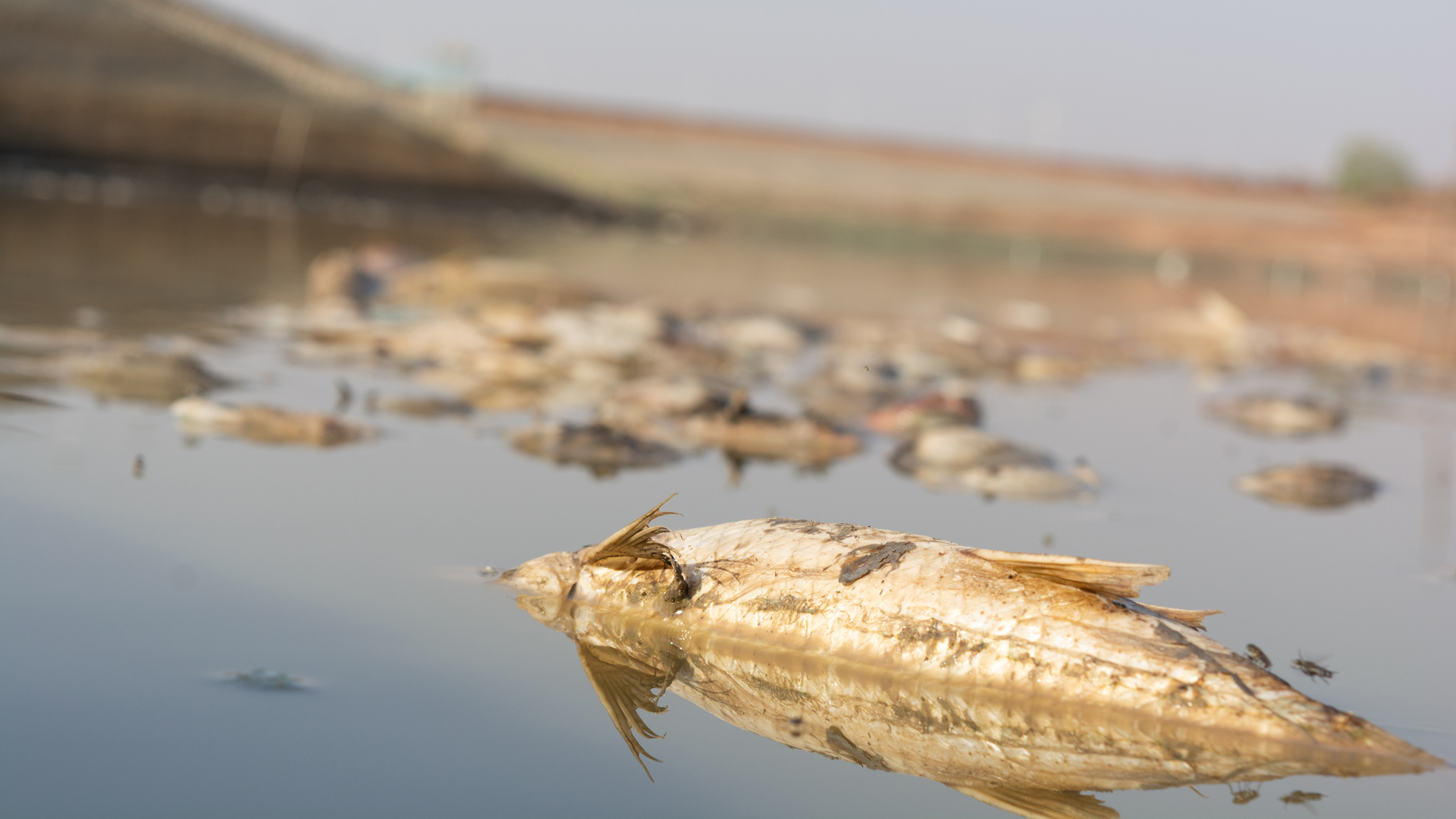 Figure. Dead fishes as a consequence of a summer heatwave with low rainfall.
Figure. Dead fishes as a consequence of a summer heatwave with low rainfall.
Pilot 3
Monitoring river connectivity and impact on biodiversity.
Detailed Pilot 3 information can be found here: BIOMONDO_Pilot3.pdf
Human-made waterworks such as dams change and affect the natural flow regimes, dispersal routes and habitats of aquatic and semi-aquatic species in rivers and river floodplains. They can also influence the water quality and natural sediment transport. Biodiversity in lake and river ecosystems are vulnerable to these connectivity changes.
The pilot objective is to explore the possibilities of combining EO data and modelling for monitoring and assessing the impact of dam construction and their removal on biodiversity, including effects on habitat fragmentation, dispersal routes, changes in habitat extent and water quality.
Summary of results: BIOMONDO_Science_Brief_Pilot3.pdf
Pilot 3 - site
The Greater Mekong region is the primary site for this pilot. It holds irreplaceable riches, ranging from rare wildlife in spectacular natural landscapes to communities with distinct cultural heritages. It contains some of the most biologically diverse habitats in the world and the world's largest inland fishery. 56 dams have been reported (Wikipedia, 2016) to be in use for hydropower energy in the Mekong River basin and another 31 dams were under construction. Most of the dams have been built after 1994 and more than 33% of them after 2009, and critical percolation points with respect to habitat fragmentation and biodiversity might already have been passed.
Pilot 3 - showcase
Policy Relevance:
- EU Biodiversity Strategy 2030 (EU BS)
- CBD Global Biodiversity Outlook-5 (CBD GBO-5)
Several policies include goals and targets that require action to improve river flows and freshwater habitats, such as the EU BS Restoration Plan "Restoration of 25,000 km of rivers into free-flowing rivers by 2030" and actions related to the UNEP GBO-5 Sustainable Freshwater Transition. Using historical EO data it is possible to assess the pilot site in almost unregulated condition, while more recent EO data in combination with modelling can explore the situation after 2016.
The outcome of the pilot will be used to demonstrate how the results can support EU BS and CBD GBO-5 by improving status of current dam datasets and monitoring effects on biodiversity of restoration and dam removal actions. It will support the analysis of environmental flows and critical percolation points and contribute to monitoring of effects on the water extent and quality before and after dam removal.
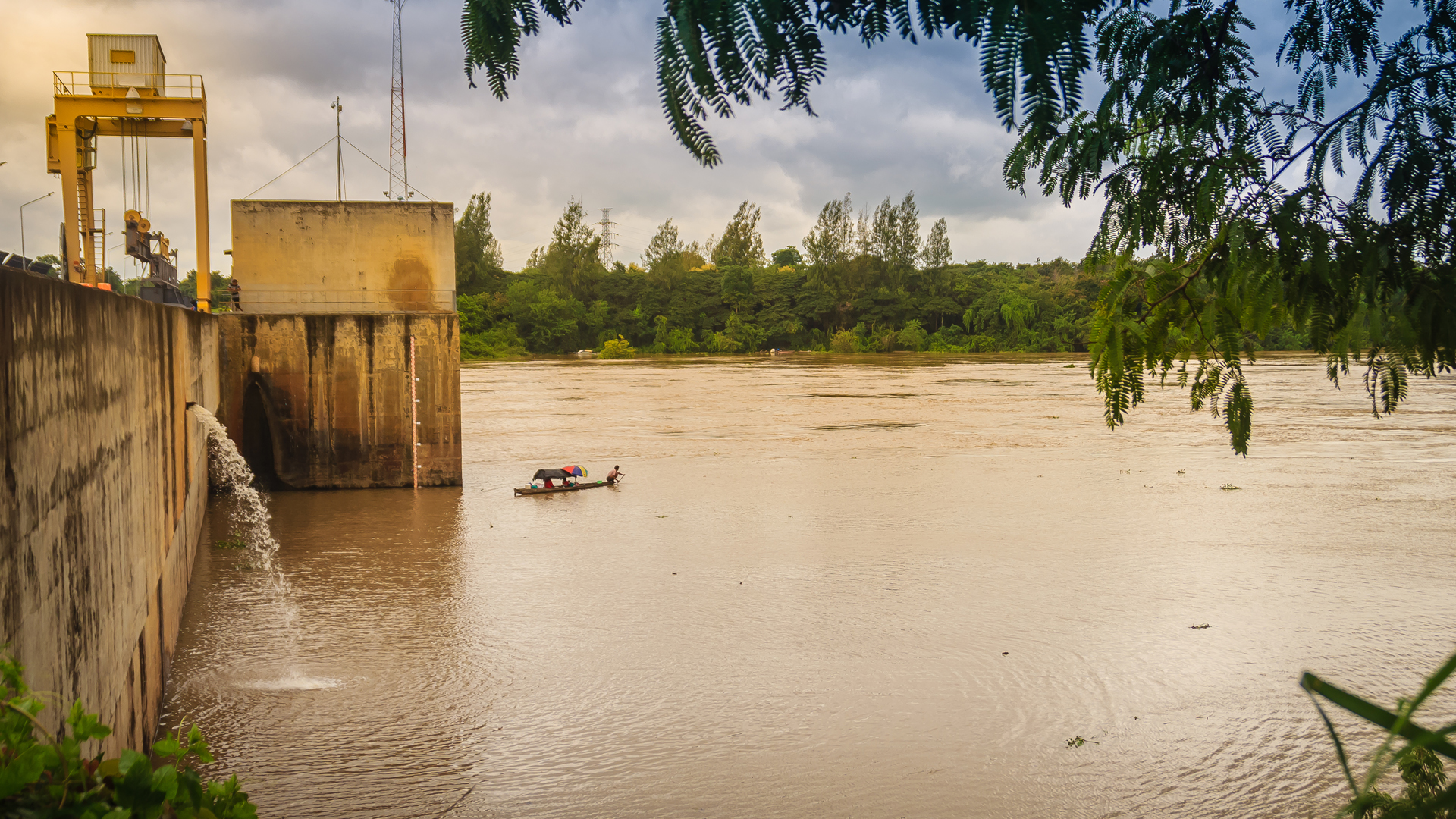 Figure. Fisherman on boat checking fishing nets at the rear of Pak Mun Dam in Thailand.
Figure. Fisherman on boat checking fishing nets at the rear of Pak Mun Dam in Thailand.
Consortium
Brockmann Geomatics
Brockmann Geomatics (BG) is a private company of geoinformatic consultants, offering services comprising information products and methodological solutions, based on remote sensing and GIS technology. The office is in Stockholm, Sweden. BG has a long experience of EO based R&D projects and with specific focus on operationalization and service provision during the last decade. Freshwaters and coastal waters are the main application, with long term assignments for Swedish national and regional authorities.
Brockmann Consult
Brockmann Consult (BC) is a private company offering services for management of environmental data and particularly from Earth Observation. The office is in Hamburg, Germany. The domain knowledge is broad and include water as well as land application and services to national and European end users. The EO competence is complemented by professional software and operations, including widely used EO processing software like SNAP and the Sentinel Toolboxes, and Calvalus. The generation of Analysis Ready Data using datacube technology is developed by BC by its xcube ecosystem of python tools.
EAWAG
Eawag is the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology and is part of the ETH Domain, which includes two federal universities and four research institutions. Eawag is concerned with concepts and technologies for dealing sustainably with water bodies and with water as a resource. In collaboration with universities, other research institutions, public bodies, industry and non-governmental organisations, Eawag works to harmonise ecological, economic and social interests in respect of water usage.
PBL
PBL Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency, located in The Hague in the Netherlands, is the Dutch national institute for strategic policy analysis in the field of environment, nature and spatial planning. PBL is particularly experienced in analysing the causes and effects of environmental change and evaluating and assessing policies at regional, national, European and global scales. PBL bases its studies on extensive data analyses, modelling (GLOBIO) and scenario analyses.
Deltares
Deltares is an independent institute for applied research in the field of water and subsurface. The head office is in Delft, Netherlands. Deltares is active world-wide, offering smart solutions, innovations and applications for people, environment and society living in delta areas. The Deltares software Delft3D is open source and is used worldwide to answer to issues that deal with for example climate change, storm surges, flooding, water scarcity, water quality, biodiversity and ecological processes.
Advisory Board
Senior experts in various field of expertise.

Prof. Dr. Ole Seehausen
Head of department for Fish Ecology and Evolution, Eawag, and Division Head, Aquatic Ecology & Evolution, IEE, University of Bern. Expertise in fish, genetics, ecology, evolution.

Ass. Prof. Dr. Erin Hestir
Researcher at University of California. Expertise in geospatial analytics, EO, sensor networks and wetlands. Special interest in aquatic ecosystems under threat while sustaining biodiversity and other ecosystem services. Regional coordinator FW BON.

Dr. Petteri Vihervaara
Leading Scientist and Head of Unit for Ecosystem Services, Finish Environment Institute (SYKE). Expertise in biodiversity, ecosystem functioning, ecosystem services, indicators, EO. Contact point for Biodiversa+ WP2 Promote & support transnational BD monitoring, Co-lead GEO BON Development, Partner in the terrestrial Biodiversity+ Precursors EO4DIVERSITY.

Ass. Prof. Dr. Maria Vallejos
Researcher at University of Buenos Aires. Expertise in Territorial Planning, EO, LULC, Landscape Ecology, Ecosystem Services, Socio-Ecological Systems. Special interest in problems associated with agricultural expansion and land use changes. Co-lead GEO BON ES WG.

Dr. Lisa-Maria Rebelo
Researcher at Int. Water Management Institute, Colombo, Sri Lanka. Expertise in remote sensing, natural resource management, wetland monitoring and assessment. Vice Chair Ramsar Conventions Scientific and Technical Review Panel.

Dr. Victor Martinez-Vicente
Researcher at Plymouth Marine Laboratory since 2002. A bio-optical oceanographer with expertise in EO, coastal waters, autonomous platforms to collect data for satellite validation, harmful algal blooms and aquaculture. PI for the coastal Biodiversity+ Precursors BiCOME.